PRISM
Using an optimization approach which employs gradients and simultaneously considers different directions at each level, projection of features ensures coherent steering along distinct manifolds. For separate steering, using optimal gradient method investigation of diverse levels is employed for feature alignment.
How PRISM Works
Using gradient optimization alongside imposing constraints on independent representation, PRISM discovers multiple distinct routes at different levels; in sharp contrast to CAA that derives one path by computing differences. While CAA calculates just one direction toward target performance independently of others, PRISM separately identifies k such directions and integrates them into a unified manifold without overlapping or excessive loss when supervised.
This method draws upon recent research such as "Geometry of Refusal in Large Language Models" by Wollschläger.
PRISM optimizes using a combined target function that consists of four key elements: separation loss (ensuring clear differentiation among positives and negatives), independent loss (preventing blending across different experimental factors), similarity bounds (maintaining distinctness among axes rather than orthogonality) and reduction of modification for negatives (minimizing alteration to negative instances). Consistency is maintained here. "PRISM utilizes optimization with respect to a composite
When to Use PRISM
- Multi-directional Behaviors: When the behavior is mediated by multiple directions (like refusal)
- Manifold Structure: When you expect a cone or manifold geometry rather than linear
- Ablation Tasks: When you want to remove rather than add a behavior
- Minimal Side Effects: When preserving model behavior on non-target inputs is important
- CAA Insufficient: When a single direction doesn't capture the full behavior
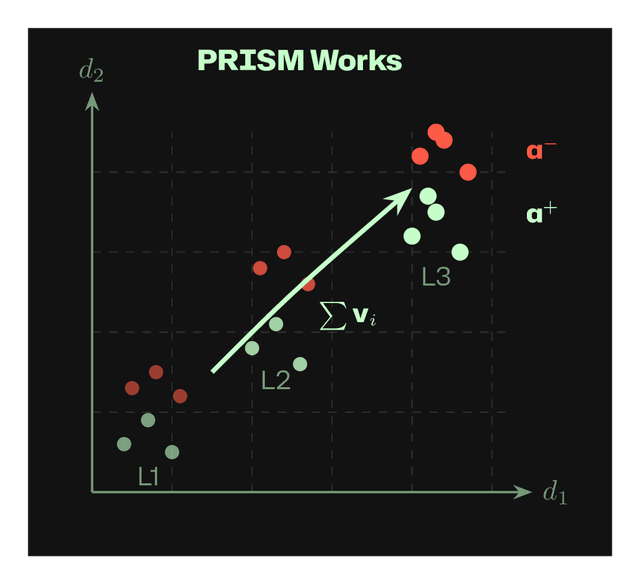
Works: Multiple layers (L1, L2, L3) each show separation. PRISM combines vectors Σvᵢ across layers.
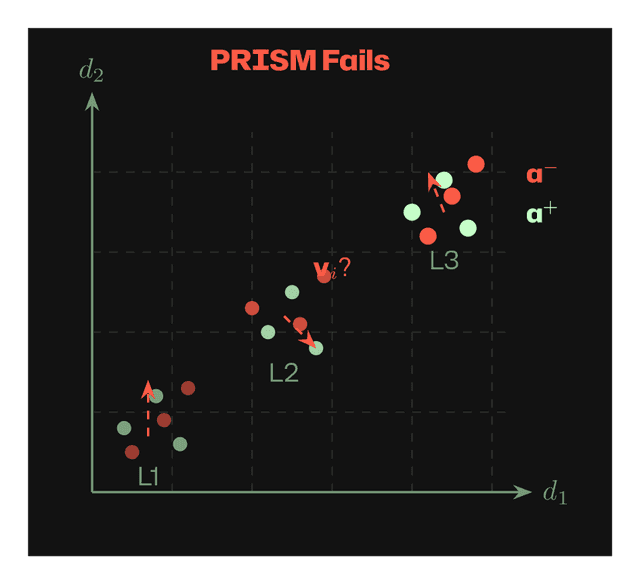
Fails: When no layer shows separation, conflicting vᵢ directions cancel out.
CLI Examples
python -m wisent.cli tasks refusal_pairs.json --from-json --steering-mode --steering-method PRISM --layer 15 --prism-num-directions 3 --save-steering-vector refusal_prism.pt
python -m wisent.cli tasks honesty_pairs.json --from-json --steering-mode --steering-method PRISM --layer 15 --prism-num-directions auto --prism-variance-threshold 0.85 --save-steering-vector honesty_prism.pt
python -m wisent.cli tasks safety_pairs.json --from-json --steering-mode --steering-method PRISM --layer 18 --prism-num-directions 5 --prism-retain-weight 0.2 --prism-independence-weight 0.1 --prism-optimization-steps 150 --save-steering-vector safety_prism.pt
python -m wisent.cli tasks bias_pairs.json --from-json --steering-mode --steering-method PRISM --layer 12 --prism-num-directions 4 --prism-use-caa-init --prism-cone-constraint --save-steering-vector bias_prism.pt
Parameters
Manifold Configuration
Optimization Parameters
Loss Weights
Constraints
For the complete implementation of the PRISM steering method in Wisent, see:
Stay in the loop. Never miss out.
Subscribe to our newsletter and unlock Wisent insights.